Ethereum (ETH): Unleashing the Potential of Decentralized Computing and Smart Contracts
Introduction:
Ethereum
(ETH) stands tall as one of the most influential cryptocurrencies, offering far
more than just a digital currency. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve
into the intricacies of Ethereum, exploring its origins, technology, use cases,
and potential impact on the future of finance and decentralized applications.
1.
The Birth of Ethereum:
1.1
The Vision of Ethereum
- Discuss the background and motivation
behind Ethereum's creation by Vitalik Buterin and the Ethereum Foundation.
- Highlight the key principles driving
Ethereum's development, such as decentralization, transparency, and
empowerment.
1.2
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin: Contrasting Approaches
- Compare and contrast Ethereum with
Bitcoin, emphasizing Ethereum's focus on programmable smart contracts and
decentralized applications (DApps).
- Explore how Ethereum expanded the
potential of blockchain technology beyond digital currencies.
1.3
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
- Explain the concept of the Ethereum
Virtual Machine (EVM) as a Turing-complete runtime environment that executes
smart contracts.
- Discuss the significance of the EVM in
enabling developers to build a wide range of decentralized applications.
1.4
The Ethereum Community
- Highlight the vibrant Ethereum community,
including developers, contributors, and enthusiasts.
- Discuss the role of the Ethereum
Foundation in supporting the ecosystem and fostering innovation.
2.
Understanding Smart Contracts:
2.1
Introduction to Smart Contracts
- Define smart contracts and their role in
automating and enforcing agreements on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Discuss the benefits of smart contracts,
such as efficiency, transparency, and elimination of intermediaries.
2.2
Programming Languages for Smart Contracts
- Explore the programming languages used to
develop smart contracts on Ethereum, including Solidity, Vyper, and others.
- Provide an overview of the development
tools and frameworks available for smart contract development.
2.3
Use Cases of Smart Contracts
- Highlight various real-world use cases of
smart contracts, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management,
identity verification, and decentralized governance.
- Discuss specific examples and success
stories in each use case category.
2.4
Smart Contract Security
- Address the importance of smart contract
security and the potential risks associated with coding vulnerabilities.
- Explain the role of code audits, formal
verification, and best practices in ensuring the security of smart contracts.
3.
Ethereum 2.0 and Proof of Stake:
3.1
The Need for Ethereum 2.0
- Discuss the scaling challenges faced by
Ethereum, including network congestion and high fees.
- Explain the goals of Ethereum 2.0 in
addressing these challenges and improving scalability.
3.2
Transitioning to Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Explain the transition from Ethereum's
current proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism to proof-of-stake (PoS) in
Ethereum 2.0.
- Discuss the benefits of PoS, such as
increased scalability, energy efficiency, and network security.
3.3
Beacon Chain and Shard Chains
- Introduce the concept of the Beacon Chain
as the backbone of Ethereum 2.0, responsible for coordinating validators and
maintaining consensus.
- Explain the role of shard chains in
parallelizing transactions and improving network capacity.
3.4
Staking on Ethereum 2.0
- Discuss the process of staking and
becoming a validator on Ethereum 2.0.
- Highlight the potential rewards and
incentives for participants in the staking ecosystem.
3.5
The Roadmap and Challenges Ahead
- Outline the development roadmap
for Ethereum 2.0 and the anticipated
milestones.
- Address potential challenges and risks
associated with the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade.
4.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) on Ethereum:
4.1
Introduction to DeFi
- Define decentralized finance (DeFi) and
its transformative potential in reshaping traditional financial systems.
- Explain the key principles of DeFi, such
as open access, permissionless innovation, and financial inclusivity.
4.2
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
- Explore the rise of decentralized
exchanges as alternatives to traditional centralized exchanges.
- Discuss popular DEXs built on Ethereum,
their features, and their impact on liquidity provision and trading.
4.3
Lending and Borrowing Protocols
- Explain the emergence of decentralized
lending and borrowing platforms, enabling peer-to-peer lending without
intermediaries.
- Discuss the benefits and risks associated
with DeFi lending protocols.
4.4
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
- Explore the concept of yield farming and
liquidity mining as mechanisms for earning rewards and incentives in DeFi.
- Discuss the risks and considerations
involved in participating in yield farming strategies.
4.5
Stablecoins and Synthetic Assets
- Discuss the role of stablecoins in DeFi,
their pegging mechanisms, and their use in lending, trading, and remittances.
- Explore the concept of synthetic assets
and their potential to provide exposure to real-world assets on the Ethereum
blockchain.
4.6
Challenges and Regulation in DeFi
- Address the challenges and risks
associated with DeFi, including smart contract vulnerabilities, security
incidents, and regulatory concerns.
- Discuss the evolving regulatory landscape
and the potential impact on DeFi platforms and users.
5.
Ethereum's Impact on Industries and Beyond:
5.1
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
- Highlight notable decentralized
applications built on Ethereum and their impact on various industries.
- Discuss DApps in areas such as gaming,
decentralized social media, supply chain management, and governance.
5.2
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Compatibility
- Discuss the importance of interoperability
in blockchain ecosystems and the efforts to achieve seamless communication
between different blockchains.
- Explore Ethereum's role in facilitating
interoperability through projects like Polkadot, Cosmos, and interoperability
protocols.
5.3
Tokenization and Digital Assets
- Explain the concept of tokenization and
its potential to transform the way we represent and trade real-world assets.
- Discuss token standards on Ethereum, such
as ERC-20, ERC-721, and ERC-1155, and their role in enabling asset
digitization.
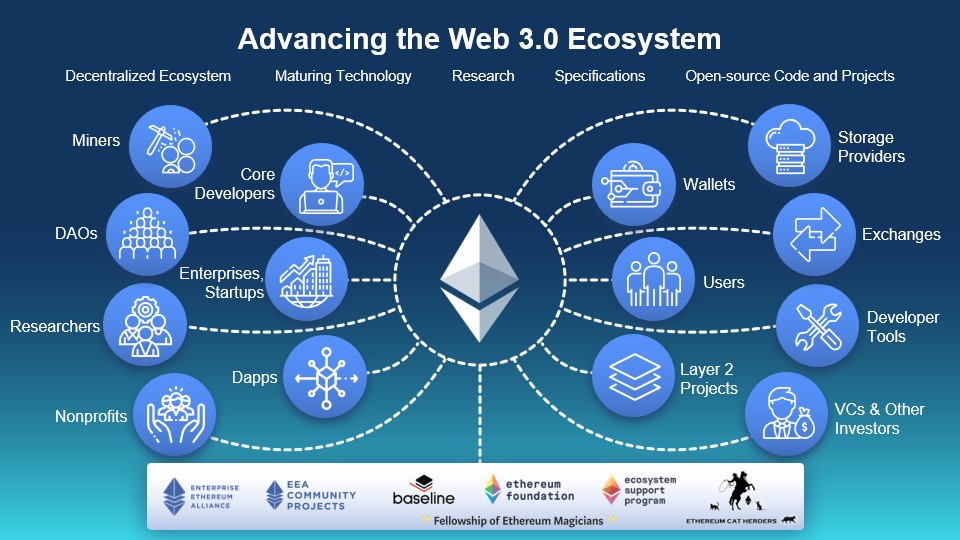
5.4
Ethereum and Web 3.0
-
Discuss the vision of Web 3.0, where decentralized applications and user-owned
data are at the core.
- Explain Ethereum's role as the
foundational platform for building Web 3.0 applications and enabling user
sovereignty.
Conclusion:
Ethereum
has emerged as a trailblazer, empowering developers and users with its robust
platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts. As Ethereum
continues to evolve, it holds the promise of transforming multiple industries
and fostering a new era of trust, transparency, and financial inclusivity. With
Ethereum 2.0 on the horizon, the scalability and efficiency of the network are
set to improve further, unlocking even greater potential. As we witness the
maturation of Ethereum and the continued growth of the Ethereum ecosystem, it
becomes increasingly clear that Ethereum is not just a cryptocurrency but a
groundbreaking technology with the power to shape the future of finance and
decentralized computing.





Comments
Post a Comment